Introduction
Activated carbon is a non-graphitic form of carbon, which could be produced by activation of any carbonaceous material such as coconut shells, bamboo, wood chips, sawdust, coal, lignite, paddy husk etc. The process of activation is carried out in two stages. The raw material is first carbonized and then activated either by chemicals or by steam to derive the highly porous structure. The two main parameters relevant to the performance of the activated carbon are namely, surface area and pore volume or structure. As to the shape of activated carbon, there is a difference between powder, granular and pelletized qualities. Based on suitable molecular size, the pore volume limits size of the molecules that can be adsorbed whilst the surface area limits the amount of material, which can be adsorbed.
Market Potential of Bamboo Charcoal
Bamboo charcoal is traditionally used as a substitute for wood charcoal or mineral coal. It can serve as a fuel, absorbent and conductor. The calorific value of bamboo charcoal is almost half that of oil of the same weight. Activated bamboo charcoal can be used for cleaning the environment, absorbing excess moisture and producing medicines. The absorption capacity of bamboo charcoal is six times that of wood charcoal of the same weight. China is a leader in its production. At present, Japan, the Republic of Korea and Taiwan Province of China are the main consumers, but its importation is rapidly expanding in Europe and North America. There are three main reasons contributing to the success of bamboo charcoal in international trade:
Industry Wise Consumption of Activated Carbon
Industry
Consumption (Tonnes)
Share (%)
Pharmaceuticals
1,968
6.0
Plasticizers
1,314
4.0
Glucose/Dextrose Monohydrate Sorbitol
1,168
3.5
Vegetable Oils
24,100
73.2
Textile & Other Sectors
4,380
13.3
Total
32,930
100
The domestic market for activated carbon is fast expanding with rapid growth of several end user industries. The demand from the vegetable oil industry- the largest consumer of activated carbon is 24,000 tonnes. The capacity utilization ratio is reported to around 85%. In such circumstances effected by higher demand as compared to shorter supply, end user industries have to depend partially on the imports and partially on the lower consumption of activated carbon at their units.
Characteristics of Bamboo Charcoal Yarns/Fabrics
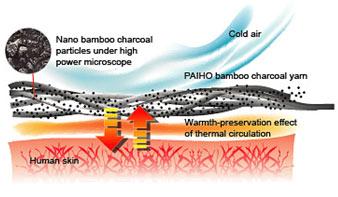
The bamboo-charcoal filament yarns have the characteristics of releasing far infrared rays and storing heat. The material, which has uniform composition and high porosity, contains abundant minerals, is antimicrobial, deodorizes, and even improves blood circulation. They have relatively better firmness and more vascular fiber tissue and thus have increased absorption. Using bamboo-charcoal filament yarns including woven ribbons (knitting and weaving), fabric for clothing, sportswear, socks, scarves, curtains, partitions, bed linens, shoe soles, and other household goods.
Bamboo-charcoal has a porous structure similar to that found in charcoal gas filters. Thus, Eco-fabric absorbs and decomposes benzene, phenol, methyl alcohol, and other harmful substances.
Unique Properties of Bamboo Charcoal Yarns/Fabrics
1) Anti-bacterial and anti-fungal property:
Bamboo-charcoal retains the natural antibacterial and antifungal traits of natural bamboo. It is also a bacteriostatic material: it inhibits bacterial metabolism, and causes fewer allergic skin reaction than other fibers sterilized with antimicrobial agents.
2) Breathable and dry property:
Bamboo-charcoal yarn has a cross-section filled with various micro-gaps and micro-holes, hence compared to other conventional fabric; it has better moisture absorption and ventilation. Eco-fabric products can absorb and disperse sweat fast, making them feel dry and comfortable. They also do not stick to skin on hot summer days.
3) Thermal regulation
Due to the porous nature of bamboo charcoal, Eco-fabric products not only feel dry during hot days, but they are also excellent insulators against the cold.
4) Absorption and emission of Far Infrared Energy
Bamboo-charcoal nano particles can absorb far infrared energy from the environment, and emit it to help cell activation, promotes blood circulation and general health in the long run.
5) Prevent static electricity buildup
As bamboo-charcoal nano particles are conductive, their presence in the fiber helps Eco-fabric prevent charge buildup. As a result, a wearer of Eco-fabric products will not experience static shocks even in dry conditions.
6) Wash Durable
As the bamboo-charcoal nano particles are embedded in the fabric rather than simply coated on their surface, Eco-fabric is washable without diminished effectiveness of the charcoal powder's special qualities, even after 50 washes.
Uses of Activated Carbon
A wide variety of activated carbon products are available exhibiting markedly different characteristics depending upon the raw material and activation of technique used in their production. In selecting the activated carbon it is important to have a clear understanding of both the adsorptive and physical characteristics of the material in order to optimize the performance capabilities.
Activated Carbon of three grades namely powder, granular and pelletalized finds hundreds of different applications. By chemical activation, predominantly powder activated carbons are made and these qualities are mostly used for wastewater treatment. Granular products and pellets used for gas purification are predominantly made by gas steam activation. To cite some examples from the numerous applications: decolourisation of sugar and sweeteners, drinking water treatment, gold recovery, production of pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals, catalytic process, off gas treatment of waste incinerators, automotive vapour filters, colour/odour correction in wines and fruit juices.
Field of Application
In its numerous applications, activated carbon represents a number of different functionalities:
Source: www.fibre2fashion.com




