High-than-expected inflation will not affect policies: bank governor
BEIJING: China's higher-than-expected inflation data hasn't altered the central bank's policy plans, bank Governor Zhou Xiaochuan said on March 14.
The central bank's interest rate stance is mainly based on the outlook for inflation and changes in the overall economy rather than published numbers, Zhou told reporters at a session of parliamentary meetings held in Beijing. He didn't elaborate on details of his policy plans.

China s central bank governor Zhou Xiaochuan is surrounded by reporters who are bombarding him with questions about the country s nancial policies for this year. [CFP]
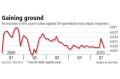
Consumer prices jumped 2.7 percent in February from a year earlier, exports surged 46 percent and industrial output gained the most in more than five years, government data showed in the past week. Economists from Goldman Sachs Group Inc, Deutsche Bank AG and JPMorgan Chase & Co said the risks of overheating were building in the world's third-largest economy and the central bank should raise interest rates as early as this month.
It's "extremely difficult" to balance growth, inflation management and the need to reform economic models, Premier Wen Jiabao said at a news conference yesterday. Inflation, income disparity and corruption combined could cause social unrest and political instability, Wen added.
Economic data, including inflation, "are a bit higher than our forecasts, but not much higher, and we can still act according to our plans," Zhou said. "Raising rates is connected to inflation figures, but from the central bank's perspective, it's not mainly based on data that have already come out."
February's inflation rate was in part caused by spending during the Lunar New Year holiday, and the year-on-year rate may slow this month, Ma Jiantang, head of the National Bureau of Statistics told reporters at the same meeting yesterday. "It's still hopeful" that the government can achieve its target to contain inflation to around 3 percent in 2010, Ma added.
Zhou reiterated yesterday that monetary policy must be "preemptive". In drafting policies, "we need data forecast in advance, because monetary policy has a fairly long lag - it takes a time lag of a few months or even one year for money supply to work into the economy," Zhou said.
Policy makers "must practice utmost prudence and also exercise flexibility" in managing the economy this year, Wen said yesterday at the end of the parliamentary meetings. To maintain "appropriate and sufficient liquidity," to keep interest rates at "reasonable" levels and to effectively manage inflation expectations are key objectives of monetary policies, Wen added.
Policy stance
While reaffirming a "moderately loose" monetary policy stance for 2010 to avoid any "setback" to the economic rebound, Wen said policies will be kept flexible "should circumstances change." It is "essential" that the timing of any policy moves is appropriate, Wen added.
China's economic growth rate quickened to 10.7 percent last quarter, the fastest pace since 2007, driven by a record 9.59 trillion yuan ($1.4 trillion) of new loans last year and 4 trillion yuan, two-year stimulus spending on railways, airports and homes. Monthly inflation may climb to a peak of 4.4 percent during this year and the full-year rate will probably be at 3.4 percent, according to economists' median forecast in a Bloomberg News survey last week.
Policies to tackle the financial crisis will end "sooner or later," Zhou said on March 6, adding that policy makers will be cautious on the timing. The central bank has asked lenders to set aside more money as reserves twice this year and aimed for lower loan growth of 7.5 trillion yuan in 2010.
Bank loans slowed to 700 billion yuan last month, after lending surged in January more than the previous three months combined, central bank data showed. Growth of the broadest measure of money supply, or M2, slowed for a third month to 25.5 percent in February from a 29.6 percent gain in November, the quickest pace in more than a decade, government data show.
Bloomberg