|
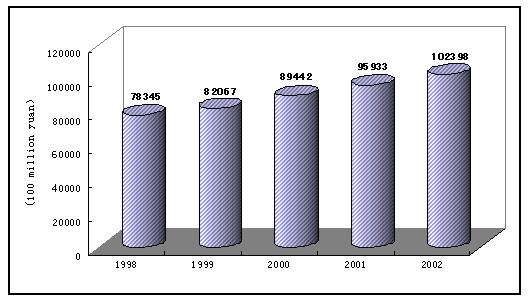
NATIONAL BUREAU OF STATISTICS PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA February 28, 2003 In 2002, under the correct leadership of the Central Party Committee and the State Council, people of all nationalities of China held high the great banner of Deng Xiaoping Theory and implemented in full swing the important thought of Three Represents . United efforts were made to work hard through innovations in a pioneering spirit and to overcome difficulties in the course of development. Main targets set forth for the economic and social development were met. The national economy maintained good momentum and a new high was scored in economic aggregates. The pro-active financial policy and sound monetary policy yielded notable results, bringing about a growing domestic demand. Initial results were achieved in the strategic structural reform of the economic system and progress was made in the optimization and upgrading of the industrial structure. Reforms in various fields deepened and China is opening wider to the outside world. New achievements were made in socialist democracy and legislation and in building up spiritual civilization. Overall progress was registered in education, science and technology, public health, sports and other social undertakings. The living standard of urban and rural households further improved along with the steady increase of their income. I. General Outlook The national economy maintained relatively fast growth. The gross domestic product (GDP) of the year topped the 10 trillion yuan level to reach 10,239.8 billion yuan, up by 8 percent over the previous year at comparable prices. The value-added of the primary industry was 1,488.3 billion yuan, up by 2.9 percent. The value-added of the secondary industry was 5,298.2 billion yuan, up by 9.9 percent. The value-added of the tertiary industry was 3,453.3 billion yuan, up by 7.3 percent. Figure 1: Gross Domestic Product Topped 10,000 Billion
The general price level declined by small margin. The general level of consumer prices in China of the year was down by 0.8 percent over the previous year. Of this total, the consumer price level in urban areas was down by 1 percent, and it was down by 0.4 percent in rural areas. Analyzed by price categories, the prices for commodities dropped by 1.3%, the producers prices for manufactured goods dropped by 2.2%, and the purchasing prices for raw materials, fuels and power went down by 2.3 percent. The prices for investment in fixed assets were up 0.2 percent. Prices of service items in household consumption rose by 1.8%. Table 1: Change in Consumer Prices over 2001 (%)
The size of employment continued to expand. By the end of 2002, the total of employed people in China numbered 737.40 million, or 7.15 million more than at the end of 2001. Of this total, 247.80 million were employed in urban areas, an increase of 8.40 million persons over that at the end of 2001. By the end of 2002, the number of laid-off workers of state-owned enterprises who were not re-employed was 4.10 million, or 1.05 million persons less than that at the end of 2001. The urban unemployment rate through unemployment registration was 4 percent at the end of 2002, up by 0.4 percentage points. China s balance of payment was in good position. The trade surplus was 30.4 billion US dollars in 2002. The actually utilized foreign direct investment during the year was 52.7 billion US dollars, up by 12.5% over 2001. By the end of 2002, China s foreign exchange reserves reached 286.4 billion US dollars, an increase of 74.2 billion US dollars as compared with that at the end of the pervious year. The exchange rate of RMB was stable, standing at 1 US dollar = 8.2773 RMB yuan at the end of the year. Steady progress was made in the reform of economic system and in the structural adjustment. Competition through the market has taken initial shape in the once monopoles sectors by deepened reform of such sectors as telecommunications, civil aviation, power generation and supply. The reform and loss-reducing of enterprises in defense industry progressed smoothly. Reforms continued in the fields of government finance and taxation, banking, social security, and circulation systems for grain and cotton. Reform of the administrative procedures for examination and approval was pushed forward. Experiments in the reform of the tax and fee collection system in rural areas were gradually expanded and notable progress was made. Positive advancement was scored in the development of the western region, with accelerated progress in the construction of infrastructure and ecological environment. Agriculture production was reoriented towards regional concentration, quality improvement and industrialization. Adjustment of industrial structure was accelerated by expanding the share of industries with high or new technologies characterized by information technology. Innovation took place in domestic trade as is reflected by the rapid development of modern circulation and distribution systems. Main problems that remained in economic performance included: the restraints on economic growth by insufficient effective demand and irrational supply structure, still high pressure for employment, problems in increasing farmers' income, the difficulties in the life of some urban and rural households, persistent market disorder, and occasional occurrence of serious accidents in production. II. Agriculture Structural adjustment for crop production was continued. To meet t changing market, the sown areas of grain was 103.99 million hectares, a decrease of 2.09 million hectares as compared with that in the previous year, and the sown areas of cotton was 4.18 million hectares, a decrease of 630,000 hectares. The sown areas of oil-bearing crops rose by 240,000 hectares to reach 14.87 million hectares, that of sugar crops increased by 150,000 hectares to reach 1.80 million hectares, and that for vegetables rose by 880,000 hectares to reach 17.28 million hectares. The production of major farm crops increased, including grain, oil-bearing crops and sugar crops, the output of vegetables continued to grow with better variety and quality, while the production of cotton decreased due to significant reduction in the sowing acreage. The total output of grain in 2002 was 457.11 million tons, up by 1 percent over the previous year. Steady progress was seen in animal husbandry and fishery. The total output of meat for the year reached 65.90 million tons, up by 4 percent. The total output of aquatic products was 45.13 million tons, up by 3 percent. Table 2: Output of Major Farm Products
Item
Output (10,000 tons)
Increase over 2001 (%)
Grain
45711
1.0
Summer crops
9877
-2.9
Early rice
3025
-11.0
Autumn crops
32809
3.5
Oil-bearing crops
2900
1.2
Peanuts
1495
3.7
Rapeseed
1053
-7.1
Cotton
492
-7.5
Sugar crops
10151
17.3
Sugarcane
8883
17.4
Beetroot
1268
16.4
Cured tobacco
213
3.9
Tea
74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Related News
Photos
More>>trade
- The Real Estate Climate Index Slightly Increased in July
- The Value-added of Industry Increased 16.1 Percent in July
- The Total Retail Sale of Consumer Goods Increased by 12.7 Percent in July
- The CPI Increased by 1.8 Percent in July
- The producers' Price Index (PPI) for Manufactured Goods Up by 5.2 Percent in
market
finance
- The Real Estate Climate Index Remain the General Level in August
- The producers' Price Index (PPI) for Manufactured Goods Increased 4.5 Percent in
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI) Increased in September
- The Total Retail Sale of Consumer Goods Increased in September
- The Value-added of Industry Rose by 16.3 Percent in September